Introduction to exchange-traded funds (ETF)

In this article, I will write about the introduction of exchange-traded funds. In the world of financial technology, we often hear about exchange-traded funds.
However, many beginners do not yet understand the meaning of exchange-traded funds. Maybe beginners are more familiar with forex and stocks than exchange-traded funds.
Before I have written about Mutual Funds. And this ETF is actually a mutual fund in the form of a Collective Investment Contract. Where the units are traded on the Stock Exchange. You can reread about mutual funds if you’re still curious about the meaning.
Best TenkoFX broker. Good forex Brokers with positive feedback of reviews from users and are regulated by IFSC Belize
Open an account or try a Demo account.
What exchange-traded funds?
Referring to Wikipedia, Exchange-traded funds or ETFs are Mutual Funds in the form of Collective Investment Contracts whose units of participation are traded on the Stock Exchange.
ETFs are basically mutual funds. But these products are traded just like the stocks on the stock exchange. On another hand that ETF is a combination of mutual funds in terms of fund management with the share mechanism in terms of buying and selling transactions.
An example of an ETF is the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), which tracks the S&P 500 Index. ETFs can contain many types of investments, including stocks, commodities, bonds, or a mix of investment types.
Exchange-traded mutual funds are marketable securities. It’s meaning that a mutual fund has a price that allows it to easily buy and sell.
ETFs refer to as exchange-traded funds just like stocks. ETF stock prices can change throughout the trading day when shares are bought and sold on the market.
This is what distinguishes ETFs and mutual funds that are not traded on an exchange. ETFs also tend to be more cost-effective and more liquid when compared to mutual funds.
ETFs are also a type of fund that has many basic assets, not just one such as stocks. Because there are many assets in an ETF, they can be a popular choice for diversification.
ETF types
There are various types of ETFs for traders to generate income, speculation, price increases, to hedge or offset risk in portfolios. These types are:
- ETF bonds include government bonds, corporate bonds, and state and local bonds or municipal bonds.
- Another type is the ETFs industry, which is tracking specific industries such as technology, banking, or the oil and gas sector.
- Then ETFs Commodity, investing in commodities including crude oil or gold.
- Next ETFs Currency, investing in foreign currencies such as Euros or Canadian dollar.
- Inverse ETF, trying to benefit from the decline in stocks by shorting stocks. Shorting is selling shares expecting a decrease in value and buying them back at a lower price.
Note that the Inverse ETF is an exchange-traded note (ETN) and not a true ETF. ETNs are bonds but traded like stocks and backed by an issuer such as a bank. Be sure to check with a broker first to determine if ETN is a good fit for your portfolio.
How exchange-traded funds work?
ETF buying and selling transactions may be made through the primary and secondary markets.
Primary market
In the primary market, investors buy and sell ETF units back to the investment manager in units. This mechanism applies to transactions with large nominal values. Slightly different from the first price of a mutual fund, the first price of an ETF can start at any price.
In general, the investment manager will make the first price of the mutual fund the same as the reference index, making it easier to monitor the comparison with the reference index.
Secondary market
Meanwhile, in the secondary market, investors can buy and sell units of ETF participation in lots. And investors buy ETFs not from an investment manager but from other investors who own the ETF at an agreed price and amount.
The drawback of the buying and selling mechanism in the secondary market is that if there is no match for the supply and demand, there is no transaction. To anticipate its condition, there are parties called participating dealers.
Participating dealers are securities companies that provide liquidity to ETFs. Dealers act as buyers and sellers when there is not enough supply and demand.
Participating dealers will enter the bid and ask for orders at market prices so that investors will have no difficulties in buying or selling ETFs on the stock exchange.
ETF flexibility
ETFs offer greater flexibility when compared to conventional mutual funds. The process of buying and selling ETFs occurs directly between the investor and the investment manager. Whereas in conventional mutual funds, investors must make transactions through an investment manager who will carry out the transaction.
Mutual fund prices are also set at the end of the trading day when the net asset value (NAV) is determined. In comparison, ETFs are subscribed or redeemed in large numbers by institutional investors, and ETF shares are traded throughout the day between investors throughout the day like ordinary shares.
ETF Liquidity
ETF is quite liquid because its liquidity is determined by the liquidity of the stocks included in the ETF product. To measure liquidity, usually look at the volume of stock traded transactions per day.
When there is very little interest and volume is traded, the spread increases, so the buyer has to pay a premium and forces the seller to give a discount to secure the sale.
Meanwhile, ETF does not face this condition because ETF liquidity is not related to the daily ETF trading volume. It is more affected by the liquidity of shares included in the ETF product.
How are exchange-traded funds managed?
Exchange-traded funds are managed through passive management and active management.
Passive management
Passive management is tracking market indices such as the S & P500, which aims to replicate the performance of these indices.
For example, an ETF that contains the 10 largest companies on the stock exchange. If the share price of each of the 10 companies rises, the overall value of the ETF will also be rising. On the other hand, if its price is down, the ETF value will down too.
Active management
Meanwhile, active ETFs are individuals will choose not by tracking an index. Here securities are selected by investment managers using a specific strategy that aims to outperform the market.
In terms of risk, active ETFs may be riskier than passive ETFs. It depends on the individual investment manager’s skills in choosing securities. If they are able to choose securities whose value increases, their portfolio investment will increase.
On the other hand, Active ETFs will typically incur higher fees because more management time is required for active investment.
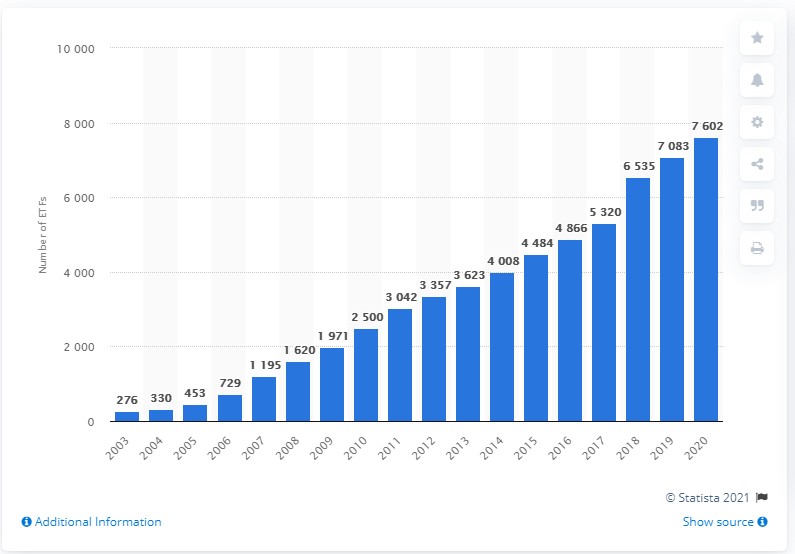
How many exchange-traded funds are there?
ETF seeing this backward began to be available on the financial market since the 1990s, this is in line with the development of internet technology so that the growth of ETF is very fast.
According to statistical data from Statista, until 2020 the number of ETFs worldwide has reached 7,602 ETF globally.
How to purchase exchange-traded funds?
ETF shares are the same as stocks that are traded through an exchange, for purchasing ETF is through certain brokers who provide access to ETF trading.
The first step to take is to register with a broker to trade ETFs.
- Choosing an ETF broker may require more understanding to compare the services of one broker to another. The fee is also a consideration for traders who will try to purchase ETFs.
- Then about the minimum deposit, it’s better to study with the broker for the minimum deposit so you can prepare the funds needed.
- The next consideration is the asset type available, not all brokers allow traders to purchase all assets simultaneously, so it is necessary to cross-check to get the expected broker.
- Also know about customer support, whether they always respond to your every question.
- The broker feature also supports the effectiveness of your trading, try not to choose a broker that is too traditional, so that it can reach your target.
The best ETF brokers according to Wikipedia are Charles Schwab and Interactive Brokers.
Decide your strategy
ETFs also fluctuate in value making it possible to face risks. Prepare a strategy for allocation for purchasing ETFs that allow you to gain or to hedge.
Bond ETFs tend to provide value stability compared to industrial ETFs, so choose a strategy that suits your goals. This will relate to capital gains because investing in ETFs is for diversification, which can automatically buy several shares in one order.
Research ETF
As is the case with stock trading and forex, doing research is important to understand the future possibilities with the value of these assets. You may need an ETF tool to help your research from ETFDB.COM. Things that need to be considered in ETF research for example is:
Index
ETFs are a collective of several stocks, so tracking the index will get an insight into how the ETF will perform in the future. NASDAQ, S&P 500, DJIA are some good indexes to start with.
Fee
Fees in buying ETFs are also a concern, where the low fees will allow you to get better short-term benefits. This also deals with the broker you are registering with and ensures that the broker allows you to buy the ETF freely.
Buy ETF
After you have to prepare for everything, don’t forget to fund your account to buy ETFs. Using the broker’s tools you can find which ticket to buy. Enter the amount that will be purchased and confirm.
After you buy an ETF you may still need some new planning in your portfolio. Regularly check your accounts and do whatever is possible to make your funds effective profitable.
Determine Exit point
After buying an ETF, of course, you won’t be holding it forever, so it’s time to determine an exit point, this will determine your gain as a result of your planning during that time.
How safe are exchange-traded funds?
Basically, all investments have risks, but ETFs are actually mostly safe because only funds are indexed on a few stocks or bonds. Some of the risks that may occur in ETF trading are:
- Possible risk of capital gains tax costs, where any Investor who sells ETFs to other Investors on the Stock Exchange may be subject to capital gains tax.
- Risk of ETF selling and buying spread. It is the difference between the selling price and the buying price.
- Liquidity risk. In some ETFs, especially new ETFs or ETFs that follow unpopular indices, it can be the case that the trading of the ETF participation unit is very illiquid.
Although ETF investment allows risk, without leverage the losses will not reach zero. It’s just that you may be at risk of losing some of your money, but that happens when the ETF value does drop when you sell.
Buying an ETF with leverage is faster risky, where if within a week the value of the ETF drops, with 2X or 3X leverage will accelerate losses when the market bears.
Where to buy exchange-traded funds?
As previously mentioned, purchasing ETFs is to register a broker that provides ETFs on their platform. Maybe on each exchange in a country, there are also brokers that provide ETF trading. The following are some of the broker’s lists for ETFs quoting from Netwallet.
-
-
- Interactive broker, minimum account $0.
- Etrade, minimum account $0.
- Stash, minimum account $0, commission $1-$9 per month.
- Wealthfront, account minimum $500, 0.25% management fee.
- Betterment, account minimum $0, 0.25% management fee.
-
Exchange-traded funds Malaysia
For ETF investment in Malaysia, you can get information on Bursa Malaysia. There is a wide variety of ETFs on the lists which is constantly being updated.
Apart from going through the official Malaysian exchange, investors can also use brokers that provide services in Malaysia, such as Etoro, Tickmil, and so on.
Besides using a foreign broker to buy foreign ETFs, investors can also use an existing local broker.
Exchange-traded funds advantage and disadvantages
Compared to mutual funds, ETFs have several advantages, here are the reviews.
Advantage
ETFs are more efficient
Once you buy one lot of ETFs, you invest in buying all the shares on an index. So that is the fastest way of diversification.
Fast and flexible transactions
After purchasing an ETF, when it matches, it means that the ETF enters into your portfolio. The difference with mutual funds, buy now, enter the portfolio maybe tomorrow.
Risk is better controllable
Since ETF is an investment with a stock index as an underlying asset, the risk is quite measurable. Losses will only be experienced if the stock index, which is the basic asset of the ETF, experiences a correction.
Transparent
The issuer periodically will announce the composition of shares in an ETF. The price information can also be viewed at any time in real-time.
Disadvantages
Fees can be higher than regular mutual funds
As explained above, this ETF transaction fee amount will refer to the brokerage or securities company fee. There are brokers which set a buying fee of 0.15 percent and a selling fee of 0.25 percent. There are also those who buy 0.20 and sell 0.30.
Meanwhile, some mutual fund selling agents have even dared to cancel the transaction fee.
Lose liquid instead on stock
Although liquidity is keep away, compare ETFs to stocks, ETFs are more liquid than stocks. So when you want to sell it at the current market price, the one who wants to buy it at your bid price is not available. In the end, if you want to sell quickly, you will sell it below the market price.
Final thought
As an investment product, ETF can be an alternative in building a portfolio with increased gain. However, to start investing in an exchange-traded fund requires research on the product it is buying. That is one way to reduce losses.
ETF is an alternative for portfolio diversification. You can also set aside a certain amount of capital to diversify funds in the forex market.
Ready forex, crypto trading? Open an account or try a Demo account.
Read more article











